Hardware specifications
* Operating System: Arch Linux
* DE: Gnome
* Graphics Platform: Wayland
* Processors: 12 × AMD Ryzen 5 2600 Six-Core Processor
* Memory: 16 GiB of RAM
* Graphics Processor: Radeon RX 580 Sapphire Nitro+
* Motherboard: ASRock B450 Pro4
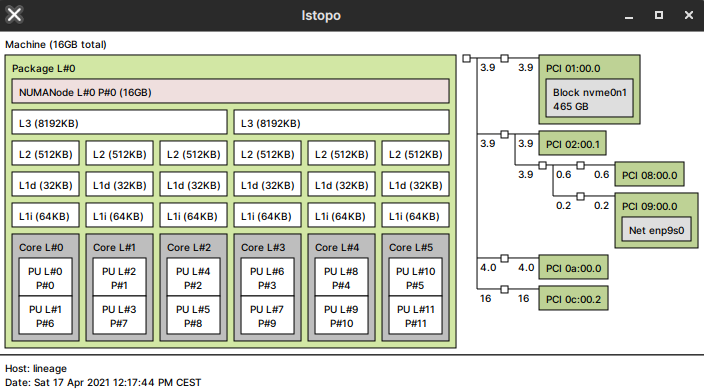
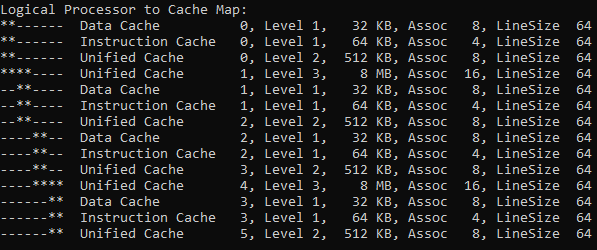
- Ryzen 5 2600 CPU Topology example
- IOMMU, libvirt, QEMU and vBIOS configuration
- Windows 10/11 virt-manager preparation and installation
- CPU Pinning
- Libvirt hooks
- Passthrough
- Logging
-
Make sure IOMMU is enabled in the BIOS. For ASRock motherboards it should be in: Advanced > AMD CBS > NBIO Common Options > NB Configuration > IOMMU
-
Append
iommu=pt iommu=1kernel parameters. If you are using the GRUB bootloader, change the/etc/default/grub:GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="loglevel=3 quiet iommu=pt iommu=1" -
Update the GRUB configuration and reboot:
sudo grub-mkconfig -o /boot/grub/grub.cfg
-
Install the necessary Arch Linux packages:
sudo pacman -S qemu-desktop edk2-ovmf libvirt iptables-nft dnsmasq bridge-utils dmidecode virt-manager
- For remote management over SSH, install this package:
sudo pacman -S openbsd-netcat
- For Windows 11 installation, you will need a TPM emulator, install this package:
sudo pacman -S swtpm
- For remote management over SSH, install this package:
-
Enable and start libvirt services:
sudo systemctl enable --now libvirtd.service sudo systemctl start virtlogd.service -
Add a user to
libvirtandkvmgroups:sudo usermod -aG libvirt kvm yourusername
-
If you want to use static hugepages:
- Check if you have the directory
/dev/hugepages. If not, create it. - Mount the hugepages in
/etc/fstaband reboot:hugetlbfs /dev/hugepages hugetlbfs mode=01770,gid=kvm 0 0
- Check if you have the directory
-
Don't forget to edit:
- /etc/libvirt/libvirtd.conf
unix_sock_group = "libvirt" unix_sock_ro_perms = "0777" unix_sock_rw_perms = "0770" auth_unix_ro = "none" auth_unix_rw = "none" log_filters = "2:libvirt.domain 1:qemu" log_outputs = "1:file:/var/log/libvirt/libvirtd.log"
- /etc/libvirt/qemu.conf
user = "yourusername" group = "kvm"
- /etc/libvirt/libvirtd.conf
-
You might need to start the default network manually:
sudo virsh net-start default sudo virsh net-autostart default
-
Restart the libvirt services after every modification:
sudo systemctl restart libvirtd.service virtlogd.service
-
Dump your vBIOS with amdvbflash:
- Dump it with:
sudo amdvbflash -s 0 yourvbiosname.rom - vBIOS will be created in home directory
- Move your GPU vBIOS file to
/var/lib/libvirt/vbiosdirectory. If you don't have this directory, create it. - Set the correct permissions and ownership for your vBIOS file:
sudo chmod -R 775 /var/lib/libvirt/vbios/yourvbiosname.rom sudo chown yourusername:yourusername /var/lib/libvirt/vbios/yourvbiosname.rom
- Dump it with:
-
You can follow this virt-manager tutorial
-
Open the virt-manager and prepare Windows iso, also use the
rawimage virtio disk. For Windows 11, you need to have over 54 GB of storage space. -
Use the
Q35chipset and UEFIOVMF_CODEloader. For Windows 11, use the secure boot loaderOVMF_CODE.secboot.fd. -
Before installing the Windows, mount the virtio-win.iso disk first in virt-manager
-
For Win11 installation, add a TPM emulator in your xml file:
<tpm model="tpm-tis"> <backend type="emulator" version="2.0"/> </tpm>
-
In order to recognize virtio disk, don't forget to load virtio driver from
virtio-win.isoin the Windows installation. -
After the installation, boot into Windows and install all virtio drivers from the device manager. You can get drivers from virtio-win.iso
-
Disable
memballoonin your xml file:<devices> ... <memballoon model='none'/> </devices>
-
You should edit your xml file and test the CPU pinning before the GPU passthrough. For details check out the 6-core CPUs topology and comments below:
-
XML Config, Ryzen 2600 2 x 3-core CCX CPU Pinning example
L3 L3 | Core#0 Core#1 Core#2 | | Core#3 Core#4 Core#5 | | |0| 1 2 | | |3| 4 5 | | |6| 7 8 | | |9| 10 11 | | \ | | \ | | Reserved for Host | | Reserved for Host | | __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ | | __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ | <vcpu placement='static' current='8'>12</vcpu> <!-- I will use only 8 cores, rest will be disabled in VM and used for the HOST machine (emulatorpin) --> <vcpus> <vcpu id='0' enabled='yes' hotpluggable='no'/> <vcpu id='1' enabled='yes' hotpluggable='yes'/> <vcpu id='2' enabled='yes' hotpluggable='yes'/> <vcpu id='3' enabled='yes' hotpluggable='yes'/> <vcpu id='4' enabled='no' hotpluggable='yes'/> <!-- Workaround to use both L3 caches, check the Coreinfo --> <vcpu id='5' enabled='no' hotpluggable='yes'/> <vcpu id='6' enabled='no' hotpluggable='yes'/> <vcpu id='7' enabled='no' hotpluggable='yes'/> <vcpu id='8' enabled='yes' hotpluggable='yes'/> <vcpu id='9' enabled='yes' hotpluggable='yes'/> <vcpu id='10' enabled='yes' hotpluggable='yes'/> <vcpu id='11' enabled='yes' hotpluggable='yes'/> </vcpus> <cputune> <vcpupin vcpu='0' cpuset='1'/> <vcpupin vcpu='1' cpuset='7'/> <vcpupin vcpu='2' cpuset='2'/> <vcpupin vcpu='3' cpuset='8'/> <vcpupin vcpu='8' cpuset='4'/> <!-- Notice that after vCPU3, we defined vCPU8. We disabled 4,5,6,7 vCPUs --> <vcpupin vcpu='9' cpuset='10'/> <vcpupin vcpu='10' cpuset='5'/> <vcpupin vcpu='11' cpuset='11'/> <emulatorpin cpuset='0,3,6,9'/> <!-- Threads reserved for host machine (in my case Core#0 and Core#3) --> </cputune>
<hyperv mode='custom'> <relaxed state='on'/> <vapic state='on'/> <spinlocks state='on' retries='8191'/> <vpindex state='on'/> <runtime state='on'/> <synic state='on'/> <stimer state='on'/> <reset state='on'/> <vendor_id state='on' value='ASRock'/> <!-- The value doesn't matter --> <frequencies state='on'/> <reenlightenment state='off'/> <!-- We use only one guest. Not fully supported on KVM, disable it. --> <tlbflush state='on'/> <ipi state='on'/> <evmcs state='off'/> <!-- We do not use nested KVM in Hyper-v --> </hyperv>
<kvm> <hidden state='on'/> <hint-dedicated state='on'/> </kvm> <vmport state='off'/> <ioapic driver='kvm'/>
<cpu mode='host-passthrough' check='none' migratable='on'> <!-- Set the cpu mode to passthrough --> <topology sockets='1' dies='1' cores='6' threads='2'/> <!-- Match the cpu topology. In my case 6c/12t, or 2 threads per each core --> <cache mode='passthrough'/> <!-- The real CPU cache data reported by the host CPU will be passed through to the virtual CPU --> <feature policy='require' name='topoext'/> <!-- Required for the AMD CPUs --> <feature policy='require' name='svm'/> <feature policy='require' name='apic'/> <!-- Enable various features improving behavior of guests running Microsoft Windows --> <feature policy='require' name='hypervisor'/> <feature policy='require' name='invtsc'/> </cpu>
<clock offset="localtime"> <timer name="rtc" present="no" tickpolicy="catchup"/> <timer name="pit" present="no" tickpolicy="delay"/> <timer name="hpet" present="no"/> <timer name="kvmclock" present="no"/> <timer name="hypervclock" present="yes"/> <timer name="tsc" present="yes" mode="native"/> </clock>
<devices> ... <memballoon model='none'/> <!-- Disable memory ballooning --> <panic model='hyperv'/> <!-- Provides additional crash information when Windows crashes --> </devices>
<domain type='kvm' xmlns:qemu='http://libvirt.org/schemas/domain/qemu/1.0'> <!-- Modify virtual machine domain configuration! --> ... </devices> <qemu:commandline> <qemu:arg value='-overcommit'/> <qemu:arg value='cpu-pm=on'/> </qemu:commandline> </domain>
-
- For 8-core CPUs and 6 physical cores / 12 virtual cores setups, check this reddit post! Also check the win10.xml example file.
-
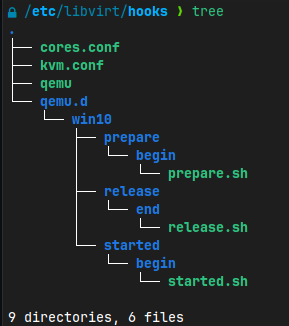
Move hooks directory from this repository to
/etc/libvirt/sudo cp -r hooks /etc/libvirt/
-
Make sure the directory name in
/etc/libvirt/hooks/qemu.d/matches the name of the virtual machine. Rename win10 if necessary. -
You will need to examine and edit the scripts.
-
You have to edit
/etc/libvirt/hooks/cores.conffile. Edit each core variable used for systemd cpu pinning. The values must match the values (vcpupinandemulatiorpincores) in the xml file. Emulator pin cores represent host machine cores, while vcpupin cores represents virtual machine cores. The variable names are self-explanatory. Also, edit masks:TOTAL_CORES='0-11' TOTAL_CORES_MASK=FFF # 0-11, bitmask 0b111111111111 HOST_CORES='0,3,6,9' # Cores reserved for host HOST_CORES_MASK=924 # 0,3,6,9 bitmask 0b100100100100 VIRT_CORES='1-2,4-5,7-8,10-11' # Cores reserved for virtual machine(s)
-
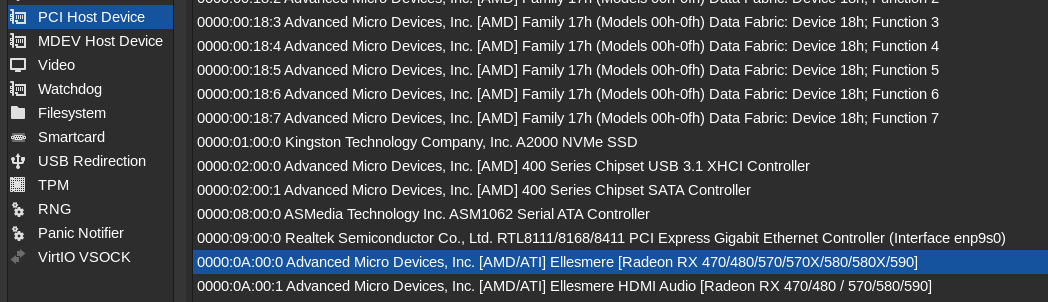
You have to edit
/etc/libvirt/hooks/kvm.conffile. EditVIRSH_GPU_VIDEOandVIRSH_GPU_VIDEOvariables. You can find VGA GPU and GPU HDMI Audio PCI IDs using thelspci -kcommand:0a:00.0 VGA compatible controller: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD/ATI] Ellesmere [Radeon RX 470/480/570/570X/580/580X/590] (rev e7) Subsystem: Sapphire Technology Limited Nitro+ Radeon RX 570/580/590 Kernel driver in use: amdgpu <- We need to unload this driver Kernel modules: amdgpu 0a:00.1 Audio device: Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. [AMD/ATI] Ellesmere HDMI Audio [Radeon RX 470/480 / 570/580/590] Subsystem: Sapphire Technology Limited Device aaf0 Kernel driver in use: snd_hda_intel Kernel modules: snd_hda_intel
-
In my case, final IDs for
0a:00.0and0a:00.1devices will be:* Final IDs * VIRSH_GPU_VIDEO: 0000:0a:00.0 * VIRSH_GPU_VIDEO: 0000:0a:00.1
-
-
The release script release.sh will set the ondemand governor. Change to schedutil governor by using the
set_schedutil_governorfunction instead of theset_ondemand_governorfunction:if [[ "$VM_ACTION" == "release/end" ]]; then release_cores # set_ondemand_governor set_schedutil_governor remove_vfio_modules load_amd_gpu restart_systemd_services fi
-
You should stop your display manager systemd service in prepare.sh script and restart it in release.sh script. I am using
gdm, so these scripts stop/restart it by default. For example, for SDDM, the recommended display manager for theKDE PlasmaandLXQtdesktop environments, you can usesystemctl stop sddm.servicecommand to stop it. Stop/restart your display manager service in thestop_systemd_services/restart_systemd_servicesfunction:stop_systemd_services() { # systemctl stop sddm.service # systemctl stop lightdm.service # --> Set your display manager instead of gdm if necessary... systemctl stop gdm.service printer "Successfully stopped systemd services" } restart_systemd_services() { # --> Restart your display manager... systemctl restart gdm.service printer "Successfully restarted systemd services" }
-
Open the virt-manager and add the GPU PCI devices, both GPU and HDMI Audio devices. Remove DisplaySpice, VideoQXL and other serial devices from the XML file:
-
<!-- Remove Display Spice --> <graphics type="spice" port="-1" tlsPort="-1" autoport="yes"> <image compression="off"/> </graphics> <!-- Remove USB Redirection --> <redirdev bus="usb" type="spicevmc"/> <redirdev bus="usb" type="spicevmc"/> <!-- Remove Video QXL --> <video> <model type="qxl"/> </video> <!-- Remove Tablet --> <input type="tablet" bus="usb"/> <!-- Remove console --> <console type="pty"/>
-
Add USB Host devices, like keyboard, mouse... You can also follow this tutorial
-
You can passthrough the PCI HD Audio controller, but be careful with adding controllers, they can be problematic. Instead, you can use qemu pusleaudio passthrough or qemu pipewire passthrough
-
In case you are using pipewire, you need to set the
connectPortspipewire-jack ports. To see the required jack ports, install the following package:sudo pacman -S jack-example-tools -
Then run the
jack_lspcommand and find the appropriate ports. -
Add one
ich9sound device with onejackaudio device and setconnectPorts, as it can be seen in the xml example, below:<sound model='ich9'> <codec type='micro'/> <audio id='1'/> <address type='pci' domain='0x0000' bus='0x00' slot='0x1b' function='0x0'/> </sound> <audio id='1' type='jack'> <input clientName='win10' connectPorts='Family 17h.*capture_F[LR]'/> <!-- The client name is usually set as the vm name --> <output clientName='win10' connectPorts='Family 17h.*playback_F[LR]'/> </audio>
-
Then modify the virtual machine domain configuration (
<domain ... >line) and add the following QEMU arguments,PIPEWIRE_RUNTIME_DIRandPIPEWIRE_LATENCY:<domain type='kvm' xmlns:qemu='http://libvirt.org/schemas/domain/qemu/1.0'> <devices> ... </devices> <qemu:commandline> <qemu:env name='PIPEWIRE_RUNTIME_DIR' value='/run/user/1000'/> <!-- Use the id command to find the correct ID --> <qemu:env name='PIPEWIRE_LATENCY' value='512/48000'/> <!-- Set desired latency --> </qemu:commandline> </domain>
-
If you cannot save changes in the virt-manager XML editor, edit with the following command:
sudo virsh edit win10. Replacewin10with your VM name. This command expects thevieditor. If you don't have it installed, you can run the command with differentEDITORlike this:sudo EDITOR=nano virsh edit vmname
-
-
Set the network source to
Bridge devicewithvirbr0device name andvirtiodevice model. -
Don't forget to add vbios.rom file inside the win10.xml for the GPU and HDMI host PCI devices, example:
... </source> <rom file='/var/lib/libvirt/vbios/yourvbiosname.rom'/> <!-- Place here --> <address/> ...
-
Check hook logs with
journalctl | grep 'libvirt-qemu' -
Check libvirt logs in
/var/log/libvirt/libvirtd.logfile -
Check qemu logs in
/var/log/libvirt/qemu/directory